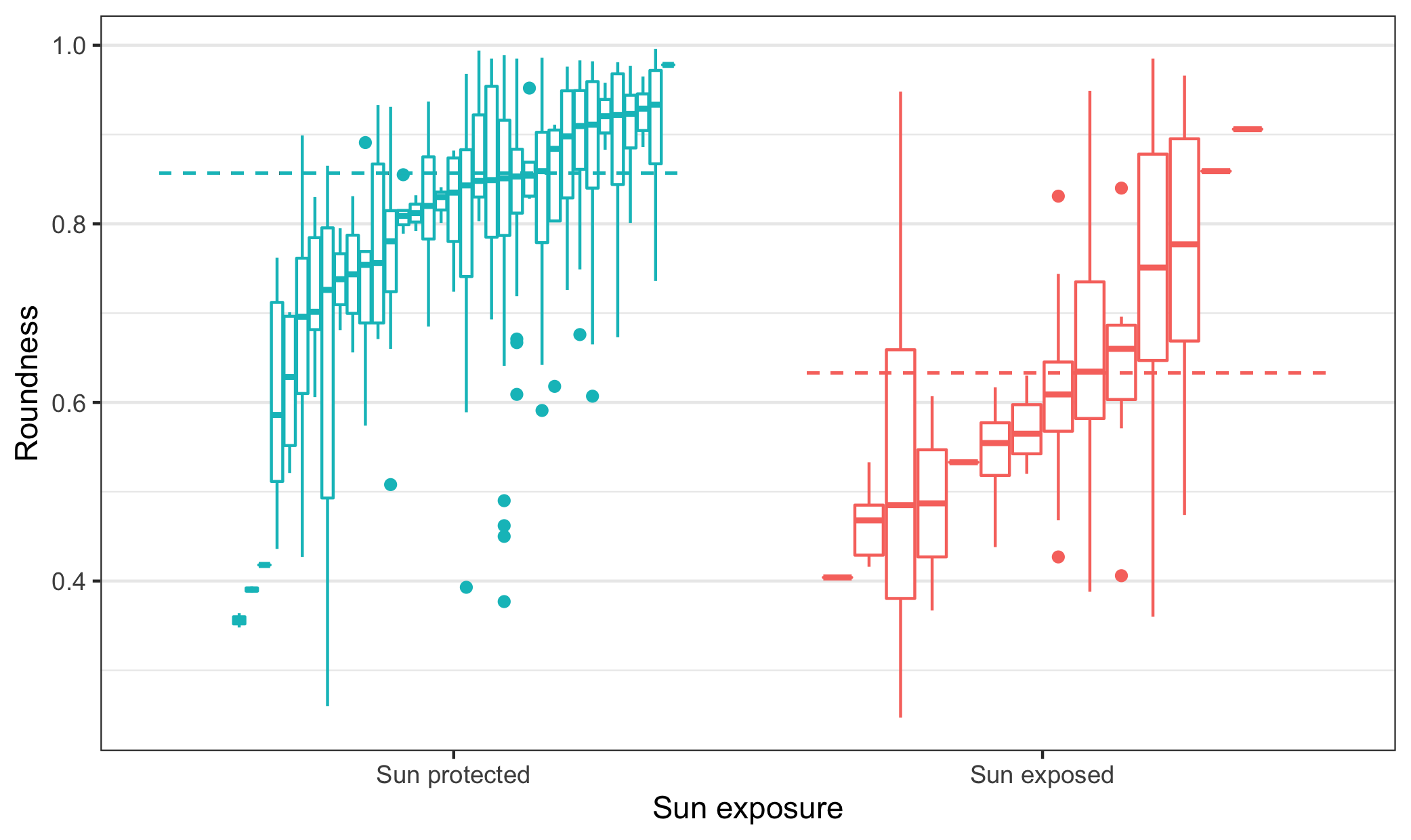
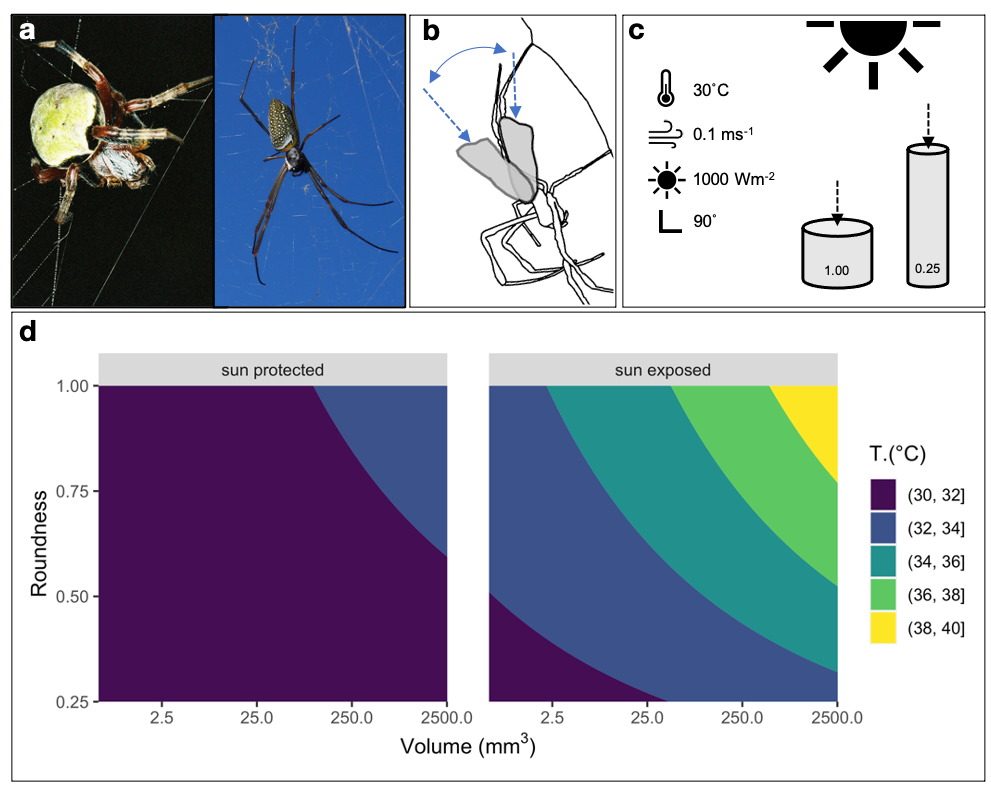
 Body temperature can strongly influence fitness. Some Sun-exposed ectotherms thermoregulate by adjusting body posture according to the Sun's position. In these species, body elongation should reduce the risk of heat stress by allowing the exposure of a smaller body area to sunlight. Therefore, selection should favour more elongated bodies in Sun-exposed than in Sun-protected species. Diurnal orb-web spider species that sit on their webs are more likely to be Sun-exposed, on average, than nocturnal or diurnal shelter-building species. We measured the body elongation of orb-web spiders (Araneae, Araneidae) across 1024 species and classified them as Sun-protected or exposed based on the literature. We found that Sun-exposed species evolved more elongate bodies than Sun-protected ones. Further, we built a model combining traditional heat transfer models with models of thermoregulatory postures in orb-web spiders and meteorological data. The model indicates that body elongation in large orb-web spiders decreases the risk of high body temperatures. Overall, our results suggest that Sun exposure influenced the evolution of body shapes of orb-web spiders.
Body temperature can strongly influence fitness. Some Sun-exposed ectotherms thermoregulate by adjusting body posture according to the Sun's position. In these species, body elongation should reduce the risk of heat stress by allowing the exposure of a smaller body area to sunlight. Therefore, selection should favour more elongated bodies in Sun-exposed than in Sun-protected species. Diurnal orb-web spider species that sit on their webs are more likely to be Sun-exposed, on average, than nocturnal or diurnal shelter-building species. We measured the body elongation of orb-web spiders (Araneae, Araneidae) across 1024 species and classified them as Sun-protected or exposed based on the literature. We found that Sun-exposed species evolved more elongate bodies than Sun-protected ones. Further, we built a model combining traditional heat transfer models with models of thermoregulatory postures in orb-web spiders and meteorological data. The model indicates that body elongation in large orb-web spiders decreases the risk of high body temperatures. Overall, our results suggest that Sun exposure influenced the evolution of body shapes of orb-web spiders.
Ferreira-Sousa, L., Rocha, P.N., Motta. P.C., and Gawryszewski, F.M. 2021. Shaped by the sun: the effect of exposure to sunlight on the evolution of spider bodies. Biology Letters, 17: 20210369, DOI: 10.1098/rsbl.2021.0369.

